Configure row-level security group membership – Deploy and maintain assets
Configure row-level security group membership
Configuring row-level security (RLS) is a two-step process. In Skill 2.2: Develop a data model, we reviewed the first step—implementing RLS roles in Power BI Desktop. In this section, we review the steps needed to complete the RLS setup for a dataset; we assign and test roles in the Power BI service.
Assigning roles in the Power BI service
Once you’ve configured row-level security roles in Power BI Desktop, you need to publish your report to the Power BI service and add members to each role. To do so, go to the dataset security settings by hovering over a dataset in the list of workspace items and selecting More options > Security. If you don’t have any roles defined in the dataset, you’ll see the message in Figure 4-2.
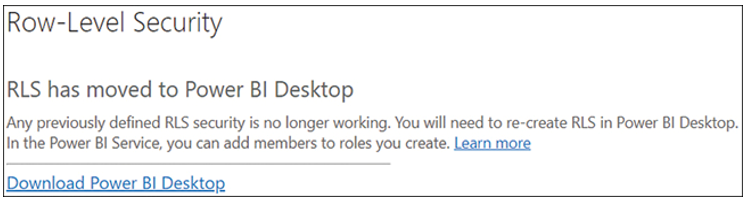
FIGURE 4-2 The RLS has moved to Power BI Desktop message.
If you’ve created RLS roles defined in the dataset, you’ll see a page like the one shown in Figure 4-3.
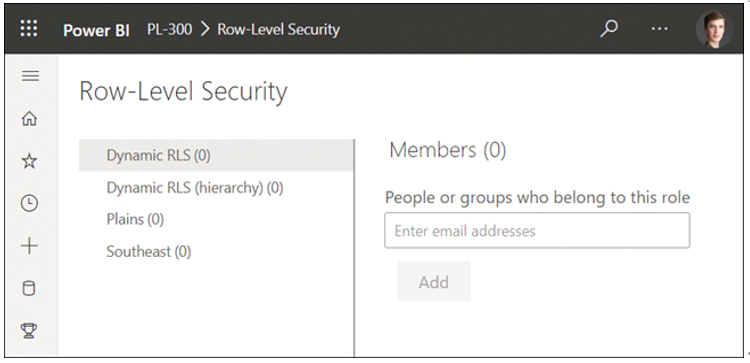
FIGURE 4-3 Row-level security role membership.
On the left side of the Row-Level Security page, you can see a list of all roles in the dataset. The numbers in brackets show how many members each role has. On the right, you can view, add, and remove members for a selected role.
To add a member to a role, first select a role on the left, and then enter email addresses or security groups in the People or groups who belong to this role field. After you enter new members, select Add > Save. The changes will be applied immediately.
To remove a member from a role, select the cross next to the member and then select Save.
When you use row-level security in Power BI, you can use an email address for each user. Although this solution works, it can be hard to maintain. For example, consider that you have several datasets that use RLS based on the same rules and it’s viewed mostly by the same users. If a new user joins your company and you need to give them access to those datasets, you will have to update the row-level security settings for each dataset.
In cases like this, you can assign security groups as members of row-level security roles. When a new user joins the company, you will have to add them to the security group only once. The same principles apply to sharing content in Power BI, which we cover later in this chapter.
Need More Review? Creating Security Groups
Instructions on how to create security groups are outside the scope of this book. For more details, see “Create a group in the Microsoft 365 admin center” at https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/admin/create-groups/create-groups.

